Charging guide: Installation of Charging Station / Charging Point
 Residual-current device / Ground fault interrupter / DC-RCM
Residual-current device / Ground fault interrupter / DC-RCM
Regulations from the Norwegian Electrotechnical Committee (NEK) require that all new electrical circuits installed after 01.01.2015, intended for charging an electric car or a plug-in hybrid, must have a type B residual-current device (RCD type B) or equivalent (DC-RCM), as well as a surge protection device (NEK 400:2018-722 standard). These requirements must be met whether you are installing a charging station, or a dedicated outlet on its own circuit for charging your electric car or plug-in hybrid (PHEV). The ground fault interrupter can be integrated into a charging station, in the fuse box or a distribution cabinet / enclosure on the dedicated power circuit.

Normally, it is the type A ground fault interrupter that is installed in homes. A type A device can be deactivated if direct current ground faults, or DC components, leak back onto the circuit. This can occur after the rectifier in the car's on-board charger (OBC). The consequence is that the coil in the ground fault interrupter (type A) becomes magnetized, and the trip current increases. This makes it difficult to know how large a ground fault needs to occur before the ground fault interrupter trips. In practice, this means that the ground fault interrupter may stop working, and you risk not detecting a ground fault that occurs, either in the car itself or elsewhere on the circuit. Such faults can occur whether you are charging in the outlet or with a dedicated charging station. Type B devices detect such ground faults, and will trip if a DC leakage occurs back on the circuit.

Installation of charging station / charging box / charging point
To meet the safety requirements and regulations, there are primarily four correct ways to install a new charging point / charging station. The power circuit should primarily be a dedicated circuit, i.e. there should be nothing else connected to the circuit, such as lights and the like. A new update in NEK 400:2018-722.305.301 now makes it possible to mount a new connection point on an existing consumer circuit for charging electric vehicles in an existing, freestanding private garage, carport or shed. However, this is only under the precondition that disadvantages with unintentional disconnection of the circuit are accepted by the owner and that the consumer circuit does not supply other connection points, and only supplies equipment and sockets installed in the immediate vicinity of the connection point (charging point) to be installed.
This means that you can connect the charging point to the same circuit as lights and sockets that are installed in the immediate vicinity in e.g. the garage. This will make it significantly easier to install a charging station / home charger in freestanding garages as the exemption significantly reduces installation costs.
However, it is very important to remember the earth fault protection. The requirements in sub-standard 722 in NEK 400 require that there should be an overvoltage protection in the fuse box, as well as an earth fault breaker type B or equivalent (DC-RCM) for the charging point. At the same time, other earth leakage circuit breakers on the circuit must be organized in such a way that they are not exposed to DC fault currents that can put them out of operation. Remember that all installation of equipment must be done by an authorized installation company.

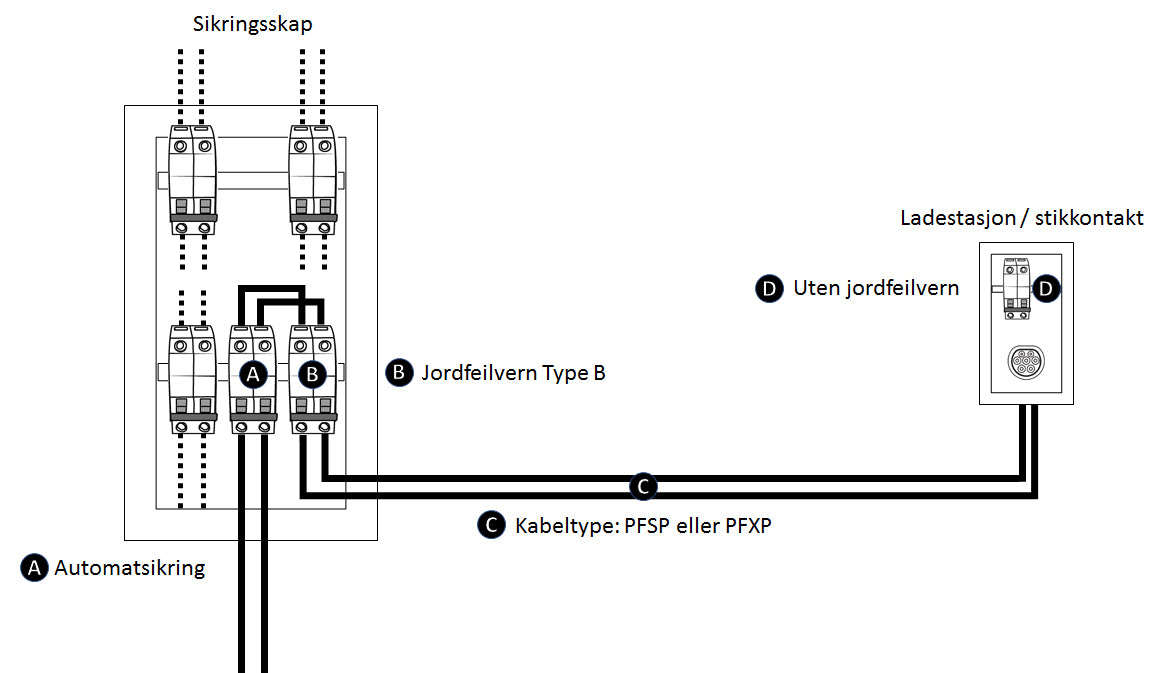
1) Earth leakage circuit breaker type B in fuse box
With an earth leakage circuit breaker Type B in the fuse box, you are free to install:
- A charging station (without B-protection)
- Regular socket (schuko) - max 10A fuse for regular socket
- Industrial socket (CEE/ EN 309) - no current limitation for industrial socket
The solution allows you to connect all types of charging units as the ELCB type B takes care of the earth fault protection. Charging stations with built-in B-protection can be installed, but it is not necessary as you have it in the fuse box. The circuit breaker is connected in series before the B-protection and you are free to use PFSP or PFXP cable.
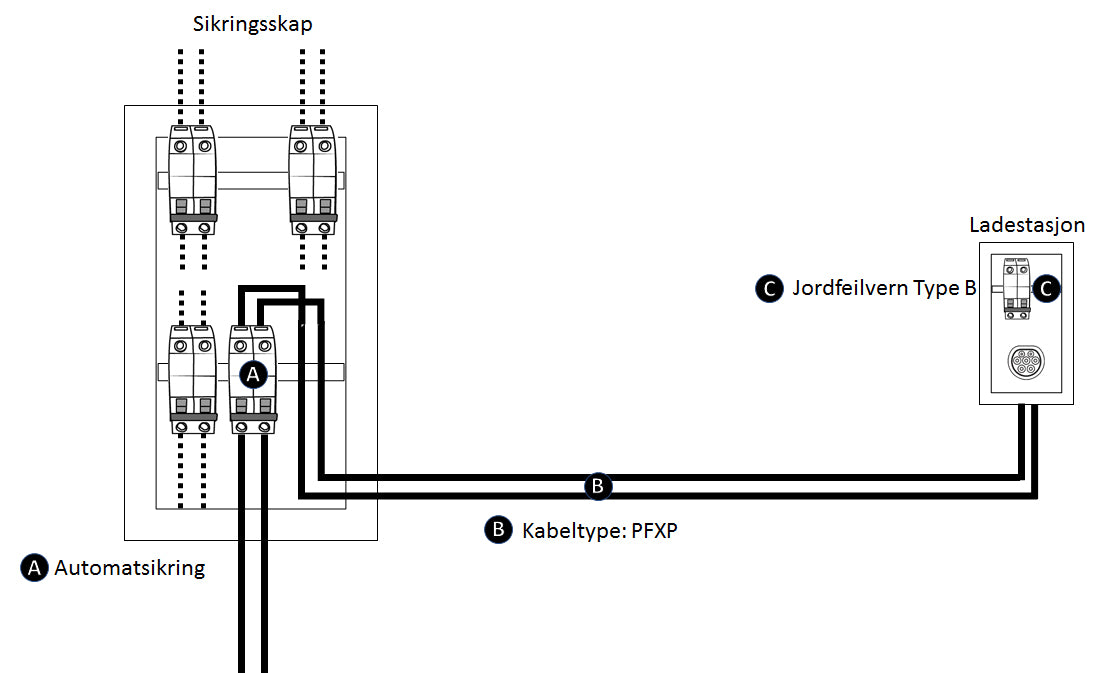
2) Type B Residual Current Device (RCD) in charging station
Installing a charging station with an integrated type B RCD means that you only need a circuit breaker in the fuse box, and a double-insulated cable must be used at the same time. Normally, PFXP cable is used, which cannot be directly buried, but must be laid in pipes when burying. At the same time, there must not be a type A RCD upstream (in the fuse box) on the circuit. This means that if one buys a charging station with built-in B-protection, the A-protection in the fuse box must be removed from the power circuit. An A-protection upstream a B-protection is not approved as DC ground faults can blind an A-protection and temporarily put the functionality of the A-protection out of operation.
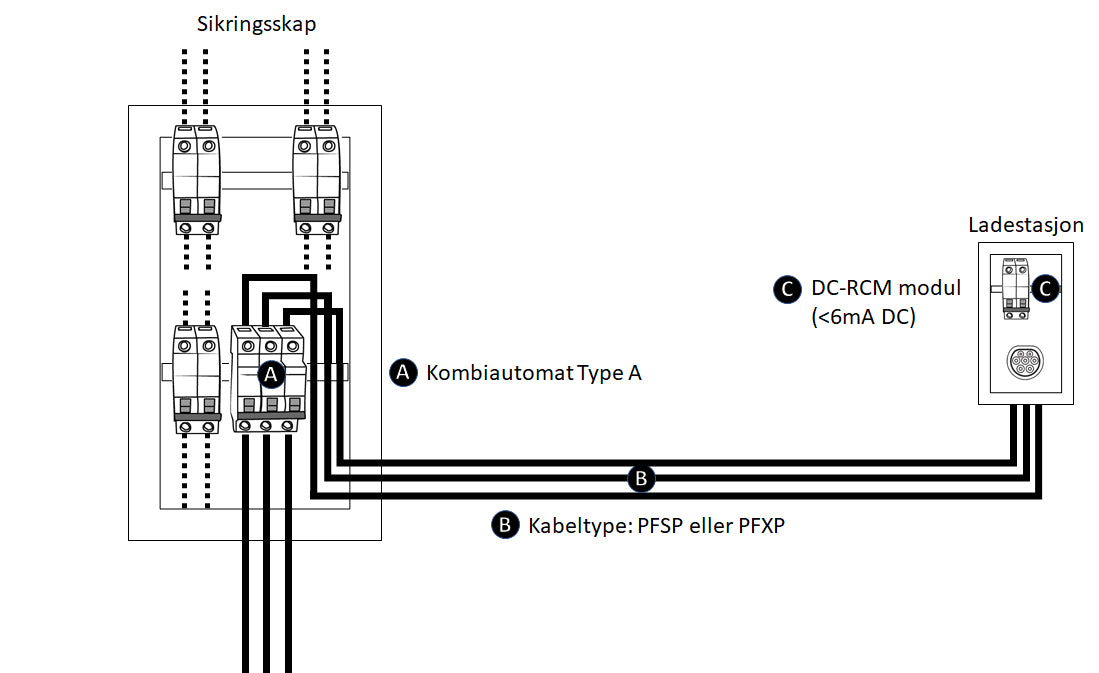
3) Type A RCD in the fuse box and DC-RCM module
Newer upgraded fuse boxes already have a combi-automatic (automatic fuse and type A RCD combined) in the cabinet/power circuit and by using a charging station/charging unit with a built-in DC-RCM module, you meet the safety requirements and regulations. A DC-RCM module / DC-filter trips at <6mA direct current faults, which in combination with an A-protection becomes equivalent to a B-protection on the power circuit. Both PFSP and PFXP cable can be used for connection from the fuse box to the charging station.
4) RCD in enclosure at charging station / charging point
In many cases, there is not room for both circuit breakers and RCD in the existing fuse box. One solution may be to pull the power circuit out into a new enclosure in, for example, the garage where the RCD and possibly a circuit breaker are mounted, and then to the charging station / charging point. Cable out to enclosure must be PFXP if there is no ground fault protection on the circuit before the enclosure.
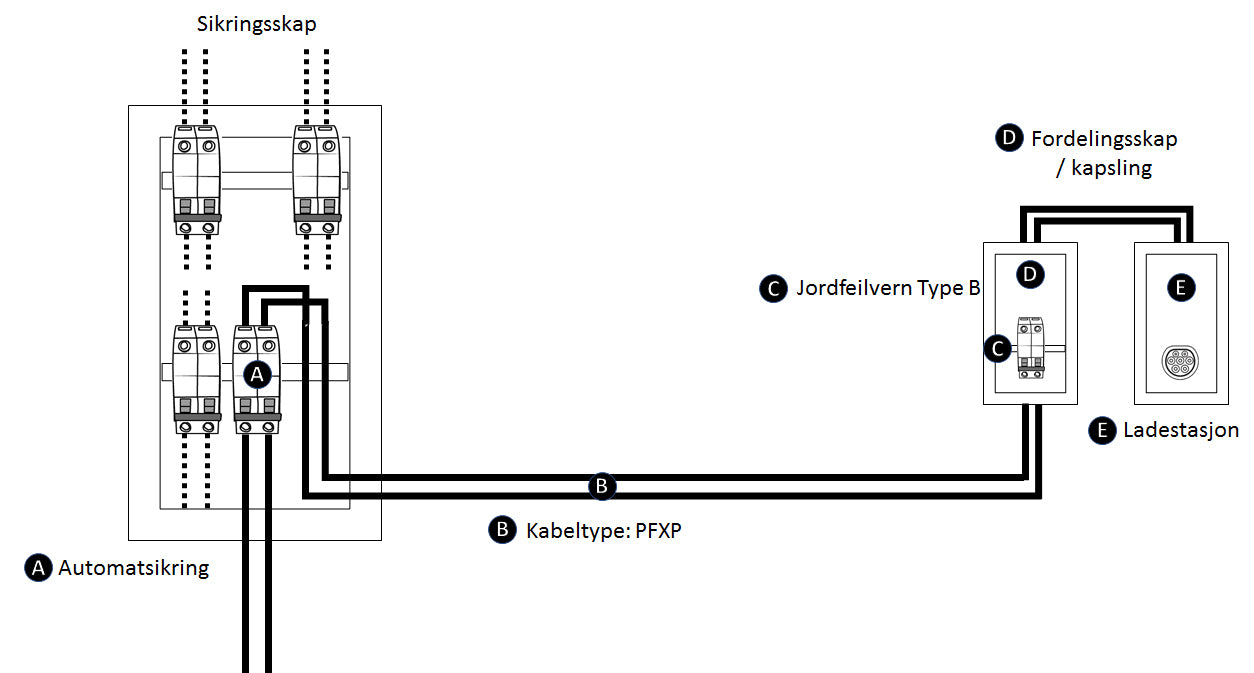
Cable Types: PFXP and PFSP
PFXP
The PFXP cable is a double-insulated installation cable with a separate ground conductor for connecting from the fuse box to the charging station. The cable comes with a single or multi-stranded annealed copper conductor that is round or sector-shaped, either 3-conductor (1-phase), 4-conductor (3-phase 230V), and 5-conductor (3-phase 400V) for both indoor and outdoor use. Examples of usage areas are in open systems, cable trays, in channels and pipes - in or under plaster, outdoors on walls or in insulated walls, and as a ground cable buried with protection. For outdoor use on walls, it must be ensured that it is not exposed to shocks and impacts.
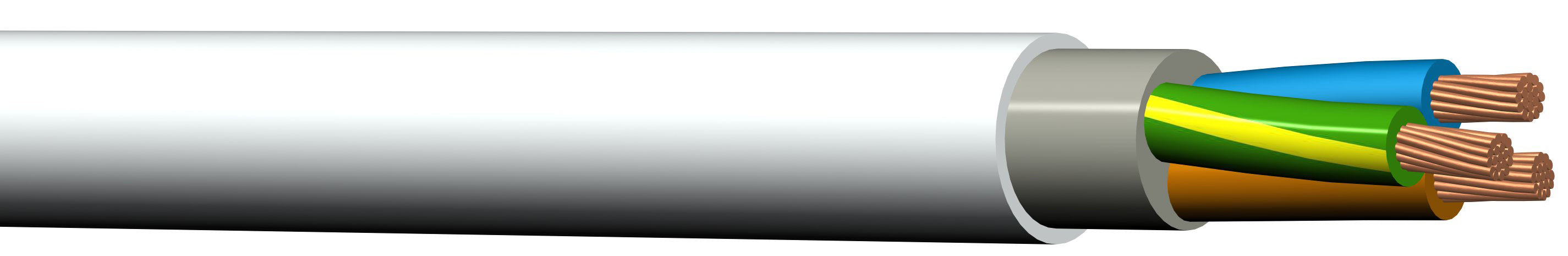

The PFXP cable must be laid in pipes when buried and is well suited in all low voltage installations, i.e., 230V, 400V, and 690V. The cable can be used as an intake cable as it is double insulated, but the PFXP cable is somewhat mechanically weak and therefore requires extra protection in the form of plates or cover boards when the intake cable is laid in the ground. The cable has an outer sheath of UV-resistant PVC for outdoor use, but the conductor insulation must be protected against direct UV light which can occur when used in, for example, light signs and lighting fixtures.
PFSP
The PFSP cable is a shielded installation and ground cable that comes with a single or multi-stranded annealed copper conductor that is round or sector-shaped, single-stranded (EN) or multi-stranded (FR). With a cross-section of 1.5–6 mm2, the concentric conductor (the screen) consists of an aluminum band where the ground conductor is placed directly under the band and in contact with it along the entire length of the cable. The concentric conductor consists of round copper wires with a counter-spiral of copper wire at a cross-section above 6 mm2. PFSP can be used both indoors and outdoors, and can be laid in all kinds of rooms and installations in addition to metal structures. Outdoors, PFSP can be used as a ground cable where it can be laid directly in the ground without the use of conduit. If you want extra protection against mechanical wear, the cable can be laid in a pipe.

The PFSP ground cable has a copper screen that is dimensioned so that it meets the criteria for ground conductors (PE) or combined ground and neutral conductors (PEN). The PFSP cable can be used in all low-voltage systems, i.e., 230V, 400V, and 690V, but the cable cannot be used as an intake cable. PFSP has lead-free PVC insulation and an outer sheath of lead-free PVC.
Cable Cross-Section
The cable cross-section on power circuits in the table is given under the conditions that the cable should be maximally loaded with 80% of maximum capacity. Likewise, with longer cable lengths, voltage drop, short-circuit currents should be considered, and larger cable cross-sections should be used. The table is only guiding (rule of thumb) and your local electrician will be able to help you choose the correct cross-section based on the conditions you have.
| Cross-section of the cable mm² | PFSP / PFXP current carrying capacity A2 (A) | TFXP current carrying capacity A2 (A) |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5mm² | 18.5A | 25A |
| 4mm² | 25A | 33A |
| 6mm² | 32A | 42A |
| 10mm² | 43A | 57A |
| 16mm² | 57A | 76A |
| 25mm² | 75A | 99A |
Installation / mounting of charging station
Please feel free to contact one of our installation partners for the installation of your charging box. By using them, you get electricians who know their craft and who perform it according to current standards and requirements. We also have installation packages you can buy along with the charging station and when purchasing such a package the electrician will contact you and arrange a time for installation.
If you need advice and tips on which charging station to choose, which installation you should/can go for, you are warmly welcome to contact us.
Law on condominium ownership (Condominium Act)
A new Condominium Act came into effect on January 1, 2018 and §25 first paragraph follows: "A section owner can, with the consent of the board, install charging points for electric cars and rechargeable hybrids in connection to a parking space the section has at disposal, or other places that the board indicates. The board can only refuse to consent if there is a valid reason". This means that condominiums and housing cooperatives cannot refuse shareholders to set up charging points for electric cars in, for example, a common garage. However, a minimum installation of Mode3 equipment with type 2 contact (universal charging point) should be installed, where there is a minimum 16A spare capacity in the installation. Provision should be made or facilities should be prepared for balancing the load using smart control.
 FedEx delivery in the EU
FedEx delivery in the EU